lunes, 22 de abril de 2013
Devolución de Vueltos En Visual Basic
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1
{
public partial class Form5 : Form
{
public Form5()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
double monto, cant, cambio, x;
int d20=0, d10=0, d5=0, d1=0, m50=0, m25=0, m10=0, m5=0, m1=0;
monto = Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text);
cant = Convert.ToDouble(textBox2.Text);
cambio = cant - monto;
x = cambio;
label12.Text = Convert.ToString(x);
//do
//{
while (x >= 20)
{
d20 = d20 + 1;
x = x - 20.00;
}
while (x >= 10)
{
d10 = d10 + 1;
x = x - 10.00;
}
while (x >= 5)
{
d5 = d5 + 1;
x = x - 5.00;
}
while (x >= 1)
{
d1 = d1 +1;
x = x - 1.00;
}
while (x >= 0.50)
{
m50 = m50 + 1;
x = x - 0.50;
}
while (x >= 0.25)
{
m25 = m25 + 1;
x = x - 0.25;
}
while (x >= 0.10)
{
m10 = m10 + 1;
x = x - 0.10;
}
while (x >= 0.05)
{
m5 = m5 + 1;
x = x - 0.05;
}
x = Convert.ToDouble(System.Math.Round(Convert.ToDecimal(x), 2));
while (x >= 0.01)
{
m1 = m1 + 1;
x = x - 0.01;
x = Convert.ToDouble(System.Math.Round(Convert.ToDecimal(x), 2));
}
//}
//while (x > 0);
label3.Text = Convert.ToString(d20);
label4.Text = Convert.ToString(d10);
label5.Text = Convert.ToString(d5);
label6.Text = Convert.ToString(d1);
label7.Text = Convert.ToString(m50);
label8.Text = Convert.ToString(m25);
label9.Text = Convert.ToString(m10);
label10.Text = Convert.ToString(m5);
label11.Text = Convert.ToString(m1);
label12.Text = Convert.ToString(x);
}
private void Form5_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
}
}
Numeros Naturales a Numeros Romanos En Visual Basic
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox2.Text = "";
int num, x, uni, dec, cen;
float div;
String[] Unidad = { "", "I", "II", "III", "IV", "V", "VI", "VII", "VIII", "IX" };
String[] Decena = { "", "X", "XX", "XXX", "XL", "L", "LX", "LXX", "LXXX", "XC" };
String[] Centena = { "", "C", "CC", "CCC", "CD", "D", "DC", "DCC", "DCCC", "CM" };
num = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
uni = num % 10;
dec = (num / 10) % 10;
cen = (num / 100) % 10;
textBox2.Text = Centena[cen] + Decena[dec] + Unidad[uni];
}
}
}
New Generation Of Programmers: Numero Par e Inpar En Visual Basic
New Generation Of Programmers: Numero Par e Inpar En Visual Basic: Public Class Form1 Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Dim numero As Intege...
Numero Par e Inpar En Visual Basic
Public Class Form1
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim numero As Integer
numero = Val(TextBox1.Text)
If (numero Mod 2 = 0) Then
TextBox2.Text = "Es Par"
Else
TextBox2.Text = "Es Impar"
End If
End Sub
Private Sub Button2_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click
TextBox1.Text = " "
TextBox2.Text = " "
End Sub
Private Sub Button3_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click
End
End Sub
End Class
Identificar El Numero Mayor En Visual Basic
Public Class Form1
Private Sub button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles button1.Click
Dim num1 As Integer, num2 As Integer, num3 As Integer, num4 As Integer
num1 = Val(textBox1.Text)
num2 = Val(textBox2.Text)
num3 = Val(textBox3.Text)
num4 = Val(TextBox4.Text)
If num1 > num2 Then
If num1 > num3 Then
num4 = num1
TextBox4.Text = num1
Else
num4 = num3
TextBox4.Text = num3
End If
ElseIf num3 > num2 Then
num4 = num3
TextBox4.Text = num3
Else
num4 = num2
TextBox4.Text = num2
End If
End Sub
Private Sub Button2_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click
textBox1.Text = " "
textBox2.Text = " "
textBox3.Text = " "
TextBox4.Text = " "
End Sub
Private Sub Button3_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click
End
End Sub
End Class
Numero Primo En Visual Basic
Public Class Form1
Private Sub button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles button1.Click
Dim residuo As Double
Dim contador As Integer
Dim i As Integer
contador = 0 'Reinicia la variable contador a cero
For i = 1 To Val(textBox1.Text)
residuo = Val(textBox1.Text) Mod i
If residuo = 0 Then
contador = contador + 1 'No puede sumar valores si estaba entre comillas "..."
End If
Next
If contador <= 2 Then
MsgBox("Es un numero primo")
Else
MsgBox("No es un numero primo")
End If
End Sub
Private Sub Button2_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click
textBox1.Text = " "
End Sub
Private Sub Button3_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click
End
End Sub
End Class
martes, 16 de abril de 2013
Area del Rectangulo En Visual Basic
Public Class Form1
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim altura As Double, base As Double, area As Double
altura = Val(TextBox1.Text)
base = Val(TextBox2.Text)
area = altura * base
TextBox3.Text = areaEnd Sub
Private Sub Button2_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click
TextBox1.Text = " "
TextBox2.Text = " "
TextBox3.Text = " "
End Sub
Private Sub Button3_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click
End
End Sub
End Class
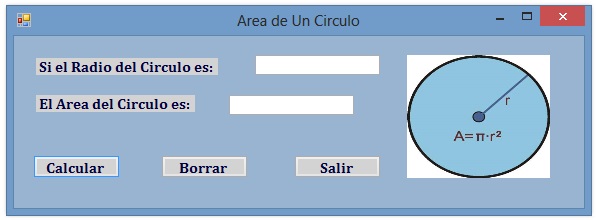
Area Del Circulo En Visual Basic
Public Class Form1
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim radio As Double, area As Double
radio = Val(TextBox1.Text)
area = Val(TextBox2.Text)
Const Pi As Double = 3.1416
radio = Val(TextBox1.Text)
area = radio * radio * Pi
TextBox2.Text = area
End Sub
Private Sub Button2_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click
TextBox1.Text = " "
TextBox2.Text = " "
End Sub
Private Sub Button3_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click
End
End Sub
End Class
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)